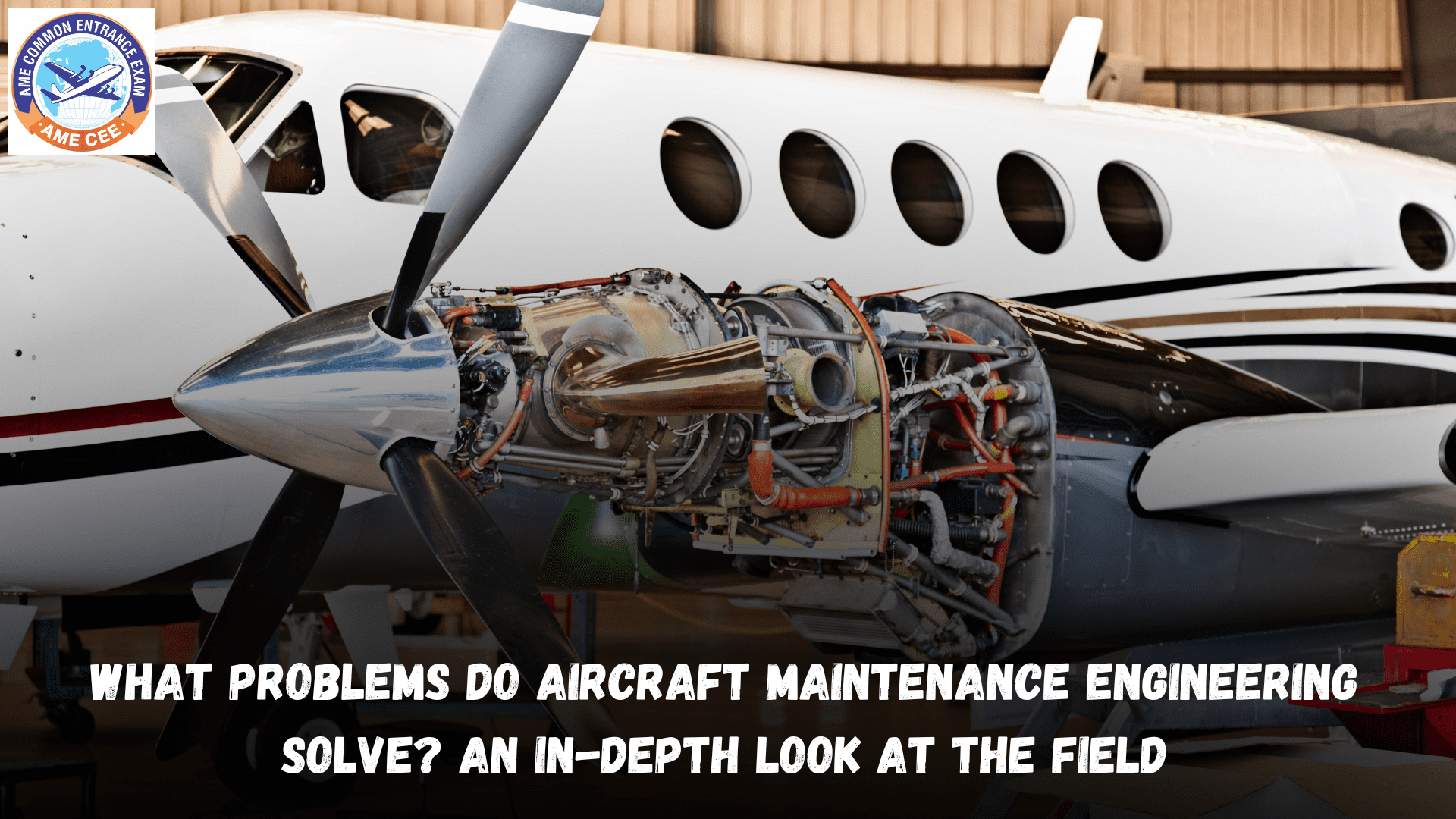
Aircraft maintenance engineering plays a vital role in ensuring the safety, reliability, and efficiency of aircraft, making it one of the most important disciplines in the aviation industry. Aircraft maintenance engineers are responsible for inspecting, maintaining, and repairing aircraft to ensure they remain airworthy and meet regulatory standards. This article provides an in-depth look at the problems aircraft maintenance engineers solve, how their work impacts the aviation industry, and the future of aircraft maintenance.
What is Aircraft Maintenance Engineering?
Aircraft maintenance engineering involves the application of engineering principles, technical skills, and aviation regulations to ensure the optimal functioning and safety of aircraft. It covers various tasks, such as routine inspections, preventive maintenance, troubleshooting, and repairs of aircraft systems, engines, and structures. Aircraft maintenance engineers are crucial in keeping both commercial and military aircraft operational, contributing to the safety and efficiency of air travel.
Key Problems Aircraft Maintenance Engineers Solve
Aircraft maintenance engineers address several complex problems that are crucial for the continued safety, performance, and longevity of aircraft. These challenges include ensuring safety, reducing downtime, improving reliability, and enhancing operational efficiency. Below are the key problems solved by aircraft maintenance engineers:
1. Ensuring Aircraft Safety
Safety is the number one priority in aviation, and aircraft maintenance engineers play a key role in maintaining safety standards. They focus on:
- Preventing mechanical failures: Engineers regularly inspect and repair components such as engines, landing gear, hydraulic systems, and electrical systems to prevent unexpected breakdowns.
- Component wear and tear: Aircraft parts undergo significant wear during flights, which can lead to failures. Engineers monitor components for signs of fatigue or deterioration and replace or repair them as necessary.
- Adherence to safety standards: Aircraft maintenance engineers ensure that all work complies with national and international aviation safety regulations, such as those set by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) or the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA).
Impact: By solving these problems, engineers help reduce the likelihood of accidents, making air travel one of the safest forms of transportation.
2. Reducing Aircraft Downtime
Minimizing the time an aircraft is out of service for maintenance is critical for airlines’ profitability and operational efficiency. Aircraft maintenance engineers work to:
- Quickly diagnose and fix issues: Engineers are trained to identify problems quickly, ensuring that maintenance work is completed efficiently and without unnecessary delays.
- Implement preventive maintenance: Routine maintenance schedules help prevent issues from developing into major problems, reducing the need for unexpected repairs and minimizing downtime.
- Efficient scheduling of maintenance tasks: Engineers collaborate with airline operations teams to ensure that maintenance is performed during off-peak hours, such as overnight, to avoid disruptions in flight schedules.
Impact: Reducing aircraft downtime increases the number of flight hours per aircraft, which boosts the airline’s revenue while minimizing delays for passengers.
3. Improving Aircraft Performance and Efficiency
Aircraft maintenance engineers are responsible for ensuring that aircraft operate at peak performance, which involves:
- Optimizing engine performance: Maintaining and tuning engines to ensure they are running efficiently, thereby improving fuel consumption, reducing emissions, and extending engine life.
- Ensuring aerodynamics: Engineers inspect and maintain the aircraft’s airframe and surfaces, such as wings, fuselage, and rudders, to ensure that they are free of damage and that the aircraft remains aerodynamically efficient.
- Upgrading systems: Aircraft maintenance engineers may upgrade avionics systems, electrical components, and software to improve overall performance, navigation, and communication capabilities.
Impact: By maintaining peak aircraft performance, engineers help reduce operational costs and increase fuel efficiency, contributing to both economic and environmental sustainability.
4. Enhancing Reliability and Longevity of Aircraft
Aircraft are expensive assets, and their longevity and reliability are key to reducing operational costs. Maintenance engineers focus on:
- Addressing corrosion: Aircraft, especially those that operate in harsh environments, are susceptible to corrosion. Engineers treat and protect components against corrosion, particularly in the fuselage, engine, and landing gear.
- Inspecting and maintaining critical systems: Critical systems like avionics, flight control, and electrical systems require frequent checks to ensure their reliability. Engineers use sophisticated diagnostic tools to detect issues before they lead to failure.
- Extended component life: Aircraft maintenance engineers ensure that components are serviced and replaced at the right intervals to extend the life of the aircraft.
Impact: Proper maintenance and regular inspections improve the longevity of aircraft, reducing the need for costly replacements and extending their operational lifespan.
5. Minimizing Aircraft Maintenance Costs
Effective maintenance practices are essential for minimizing the costs associated with aircraft upkeep. Maintenance engineers work to:
- Optimize parts inventory: Engineers work closely with supply chain teams to ensure that the necessary spare parts are available without overstocking, which can tie up capital.
- Prevent unnecessary repairs: By accurately diagnosing issues and performing preventive maintenance, engineers reduce the likelihood of costly emergency repairs.
- Implement cost-efficient techniques: Aircraft maintenance engineers use advanced tools and techniques, such as predictive maintenance powered by data analytics, to anticipate failures and address issues before they become expensive problems.
Impact: These practices help airlines and aircraft operators keep maintenance costs under control, which is critical for the profitability of airlines and other aviation companies.
6. Adapting to Technological Advancements
As technology evolves, aircraft maintenance engineering must adapt to new innovations in aviation. Engineers are responsible for:
- Adopting new maintenance technologies: Emerging technologies, such as drones for inspections, 3D printing for parts manufacturing, and augmented reality for maintenance training, are increasingly being used in the field.
- Upgrading systems and components: Engineers ensure that new technological upgrades, such as modern avionics systems and advanced communication tools, are incorporated into older aircraft models.
- Staying up-to-date with industry standards: Engineers must remain current with ever-changing aviation regulations, materials, and practices to ensure that aircraft meet new safety and performance standards.
Impact: By embracing technological advancements, aircraft maintenance engineers help improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance the safety and performance of modern aircraft.
7. Addressing Environmental Impact
As environmental sustainability becomes a priority in aviation, maintenance engineers are tasked with finding ways to reduce the environmental impact of aircraft:
- Reducing emissions: Engineers focus on maintaining aircraft engines to ensure they run efficiently and with minimal environmental impact.
- Energy-efficient technologies: Maintenance engineers incorporate energy-efficient systems and materials that contribute to a reduction in the overall carbon footprint of aviation operations.
- Sustainable practices: Aircraft maintenance engineering also includes efforts to recycle parts and use sustainable materials for repairs, such as biodegradable hydraulic fluids.
Impact: These efforts support the aviation industry’s goals to reduce its carbon footprint, promoting a more sustainable future for air travel.
8. Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Aviation is one of the most regulated industries in the world. Aircraft maintenance engineers play a critical role in ensuring that aircraft meet all local, national, and international standards:
- Regulatory compliance: Maintenance engineers must follow stringent guidelines set by regulatory bodies such as the FAA, EASA, and ICAO. They ensure that all maintenance work, repairs, and upgrades meet these standards.
- Recordkeeping and documentation: Maintenance engineers must meticulously document all work performed on aircraft, including inspections, repairs, and replacements, to maintain airworthiness certificates.
Impact: Compliance with regulatory standards ensures the safety, legal operation, and certification of aircraft, preventing costly fines or grounding of aircraft due to non-compliance.
Conclusion
Aircraft maintenance engineering is essential to the safety, efficiency, and longevity of modern aircraft. Maintenance engineers solve complex problems related to safety, performance, reliability, environmental sustainability, and cost-efficiency. By addressing these challenges, they play a critical role in ensuring that air travel remains safe, efficient, and sustainable.
As the aviation industry continues to evolve, aircraft maintenance engineers will need to adapt to new technologies, industry standards, and environmental regulations, ensuring that aircraft remain at the forefront of technological advancements while meeting the growing demand for sustainable and cost-effective air travel.